Discharge treatment plant
The plant consists of a chemical-physical pretreatment section and a final biological section for organic load removal.
THE CLIENT.
- So gi s S p A – Sospiro Cremona (IT)
- Treatment capacity: 600 m³/g
- Technology used: Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) type activated sludge chemical-physical and biological treatment
THE PROBLEM.
The plant produces fatty acid and glycerin derivatives. In 1990 SO.Gi.S entered into a joint venture agreement with Baerlocher GmbH, a world leader in the production of PVC additives. Wastewater produced from processing is treated in a physical-chemical plant with a capacity of 25 m³/h to remove suspended, colloidal solids and the insoluble fraction of organic nature For the removal of the soluble organic load, subsequent treatment of the clarified effluent is provided in an SBR-type biological plant, which is carried out in two reactors operating in parallel with a volume of 600 m³ each. The final effluent has suitable characteristics for discharge to surface water.
THE GOALS.
- The plant must operate smoothly even with changes in the incoming pollutant load;
- Continuous operation for 24h/day and 7 days/week;
- Minimize the presence of personnel for operation and maintenance;
- Ensure proper plant performance even in the absence of an initial accumulation and homogenization tank;
- Limiting operating costs (chemical reagents and electricity);
- Compliance with limits from Leg. 152/06 – Tab.3 for discharge to surface water;
THE PLANT.
PHYSICAL CHEMICAL PRETREATMENT 25 m³/h
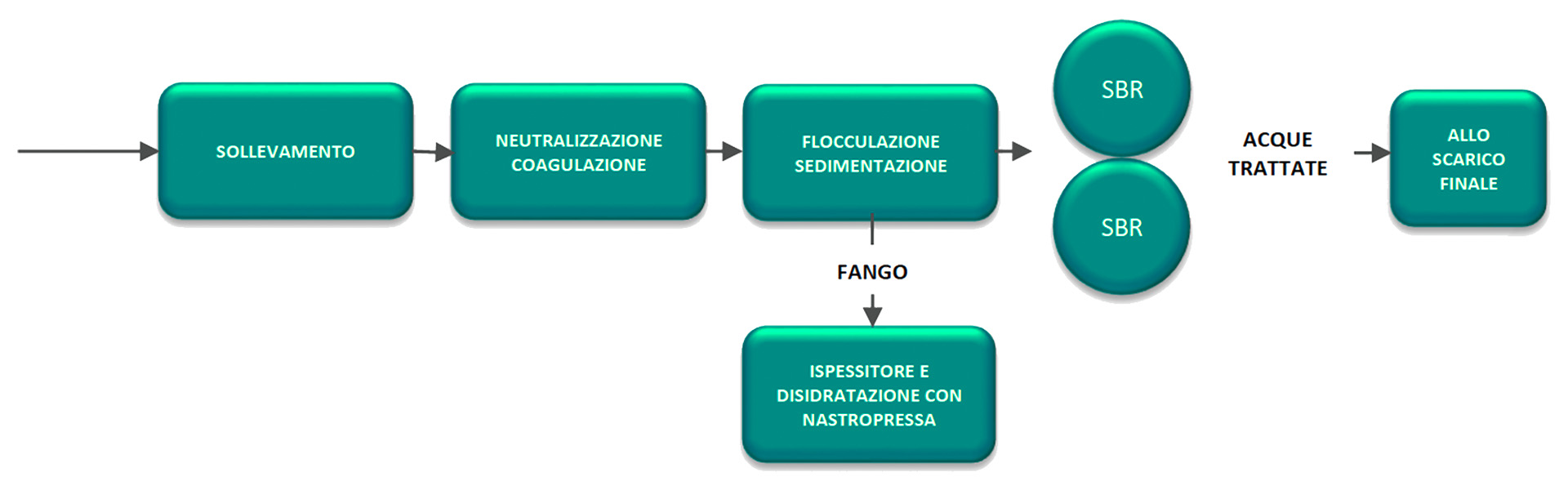
Lifting: the effluent is sent to an initial lift tank from where it is then transferred by pumps to chemical and physical treatment.
Coagulation-neutralization: The effluent is sent to a first section of the plant where the coagulation and neutralization stages take place in succession.
Flocculation-lamellar decantation: in the flocculation-decantation section, separation of suspended solids from the clarified is achieved, which is then sent to biological treatment. The sludge extracted from the bottom of the decanter is sent to the final filter press.
BIOLOGICAL 600 m³/g
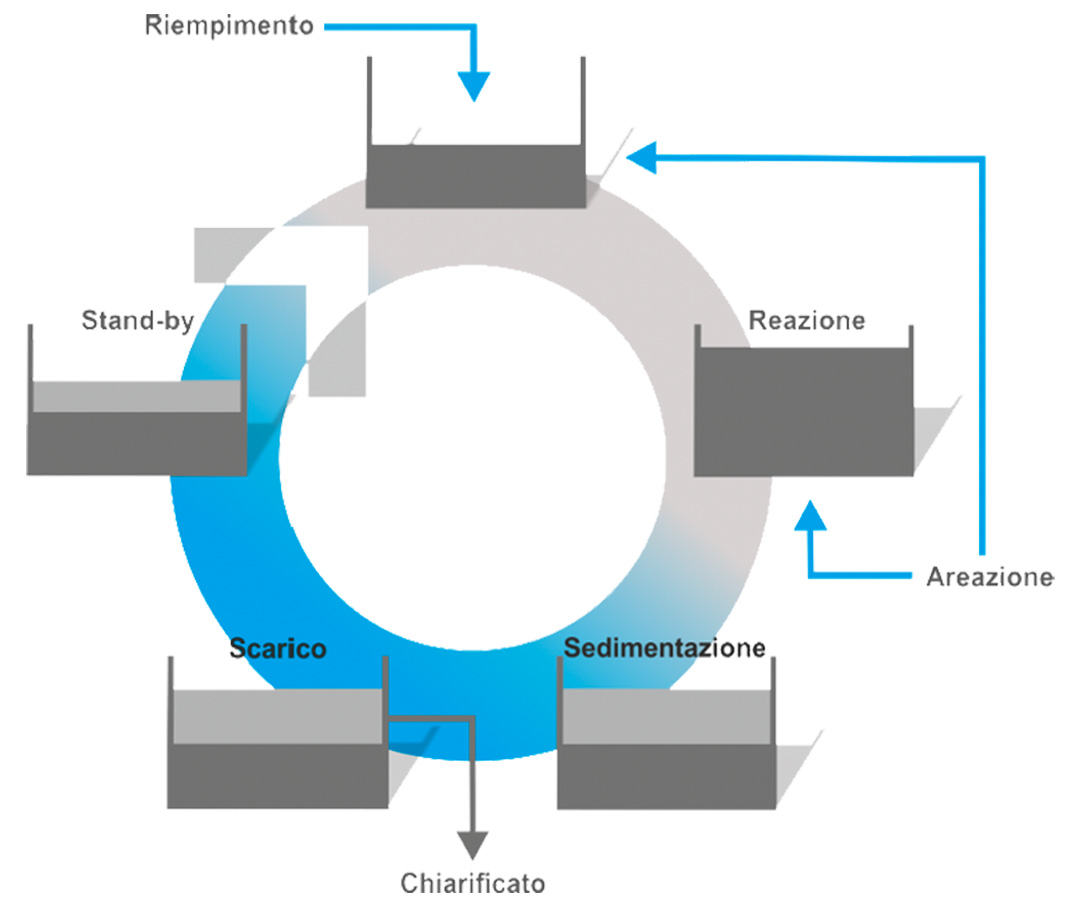
The SBR-type biological section consists of two reactors made of concrete with a volume of 600 m3 each fed in parallel. The different stages of biological treatment (accumulation, oxidation, denitrification, and decantation) occur in a temporal sequence and not spatially as in traditional biological plants (CAS, MBR, MBBR)
THE BENEFITS.
- No initial storage and homogenization tank is required for the effluent to be treated;
- High resistance to a sudden rise in organic input load;
- Absence of recirculation of both the activated sludge, as there is no settling tank, and the aerated mixture during the denitrification phase;
- High flexibility, as it is possible to change the duration of the different treatment stages, adapting them to the actual characteristics of the effluent to be treated;
- Smaller footprint than conventional biological plants;
- Ability to control and manage the plant remotely via PLC networking;
- Low consumption of chemical reagents and electricity.