Groundwater treatment plant
Plant with a capacity of 82 m³/h for the removal of hexavalent chromium and trace amounts of chlorinated solvents from groundwater.
THE CLIENT.
- Leonardo S p A Aerostructures Division, Pomigliano D’Arco, Naples (IT)
- Treatment capacity: 82 m³/h
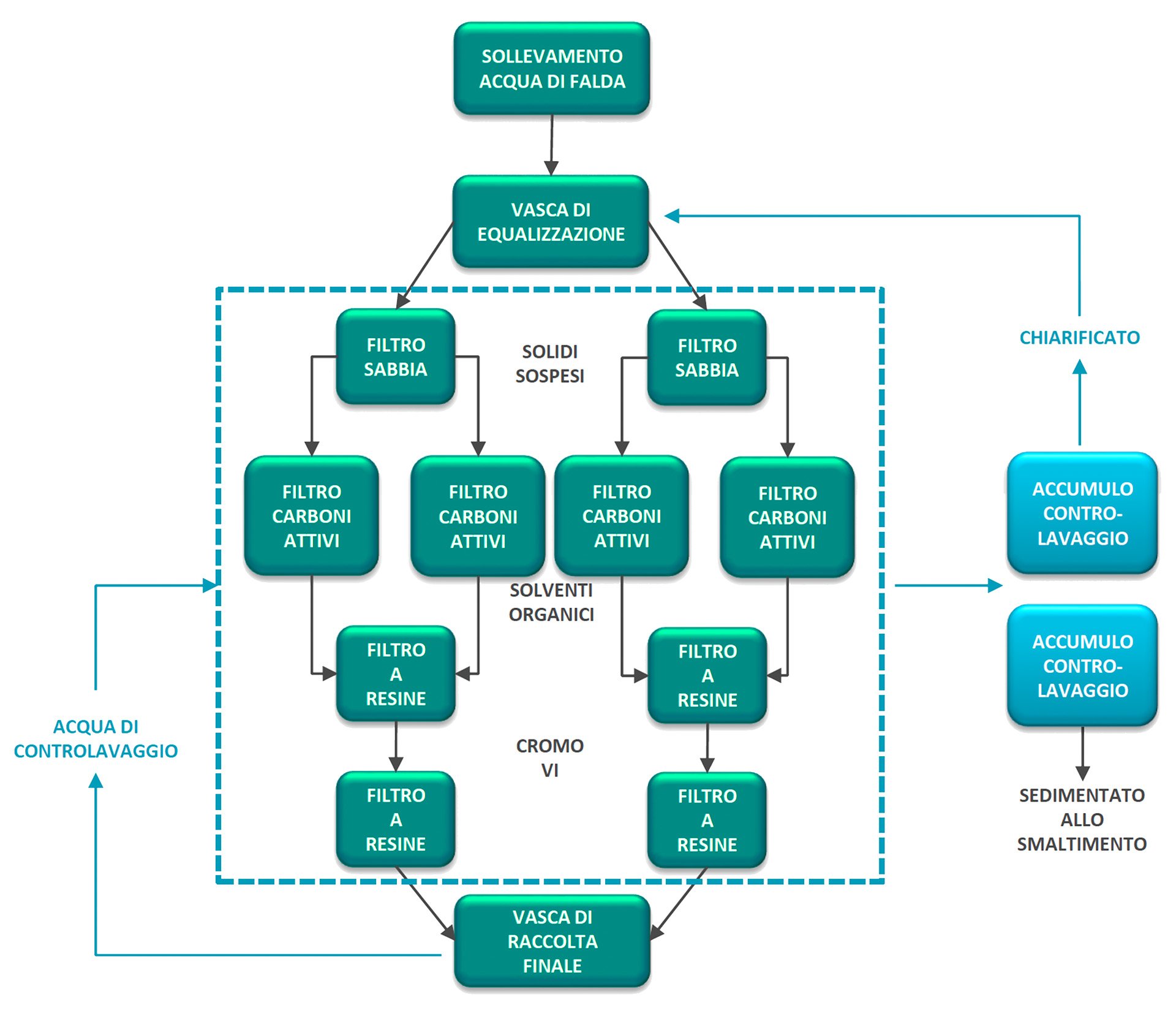
- Technology used: Filtration process on two parallel treatment lines each consisting of:
– Sand filtration for removal of suspended solids;
– Filtration on activated carbon to remove traces of organic solvents;
– Filtration on disposable selective resins for removal of hexavalent chromium.
THE PROBLEM.
On average, about 20 µg of hexavalent chromium as well as traces of several organic solvents (trichloromethane, 1,1-dichloroethane trichloroethylene, perchloroethylene) are present in groundwater.
THE GOALS.
- Lower the concentration of hexavalent chromium in the effluent from the plant below 5 µg for water reuse within the plant or final discharge
- Remove traces of organic solvents before filtration on resin
- Continuous operation of the plant for 24 hours/day and 7 days/week
- Minimizing manual interventions for plant operation and maintenance
- Ability to take advantage of the reliefs from the Industry 4.0 plan
THE PLANT.
The plant includes the following treatment stages:
- Groundwater lifting by two submersible pumps;
- Equalization in a 15 m³ volume tank;
- Taking up water with pumps and sending it to filtration with a flow rate of 41 m³/h per line.
Each line consists of:
- FILTER ON QUARTZ SAND: for removal of suspended solids that may be present in groundwater;
- TWO ACTIVATED CARBON FILTERS OPERATING IN PARALLEL: Activated carbons are provided to remove traces of organic solvents before filtration on resin;
- TWO RESIN FILTERS OPERATING IN SERIES for selective removal of hexavalent chromium;
- ACCUMULATION OF EFFLUENT for reuse within the plant or for sending to the final discharge;
BACKWASH
Water for periodic backwashing of filters is collected in two conical bottom storage tanks where sedimentation of suspended solids takes place. The solids are periodically extracted and sent for disposal, while the clarified reaches the initial equalization tank by gravity.