Impianto per il trattamento e il riciclo delle acque reflue prodotte dal recupero del vetro
The plant consists of an initial chemical-physical pretreatment section for the removal of suspended solids and a
final biological for the removal of organic load (COD and BOD₅ and nitrogen compounds).
THE CLIENT.
- Sasil S.r.l. – Integrated mining treatments, Brusnengo, Biella (IT)
- Treatment capacity: 240 m³/g
- Technology used: Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) type activated sludge chemical-physical and biological treatment
THE PROBLEM.
In the customer’s plant, processing is carried out on different types of aggregate glass, sand, granite.
The ‘wash water from these processes, is treated in an existing physical chemical plant that removes suspended solids and, very limitedly, some of the organic load. The clarified coming out of the plant is recycled for washing material. Especially during glass processing, there is a gradual accumulation of organic substances in the recycled water that compromise the characteristics of the finished product. Therefore, for the reduction of the organic load, the construction of the new chemical physical biological plant that treats the daily purging of the recycling circuit was planned. The effluent from the plant has suitable characteristics for discharge to surface water The recycling loop is replenished with industrial water so that the concentration of organic matter remains constant.
THE GOALS.
- The plant must operate smoothly even with variations in the incoming pollutant load due to different processed materials (COD 500-1300 mg/l, suspended solids 150-650 mg/l);
- Continuous operation for 24h/day and 6 days/week;
- Limiting operating costs (chemical reagents and electricity);
- Minimize the presence of personnel for operation and maintenance;
- Ability to take advantage of the reliefs from the Industry 4.0 plan;
- Discharge to surface water according to the emission limits to surface water of Leg. 152/06 Part Three – All.5 Tab.3.
THE PLANT.
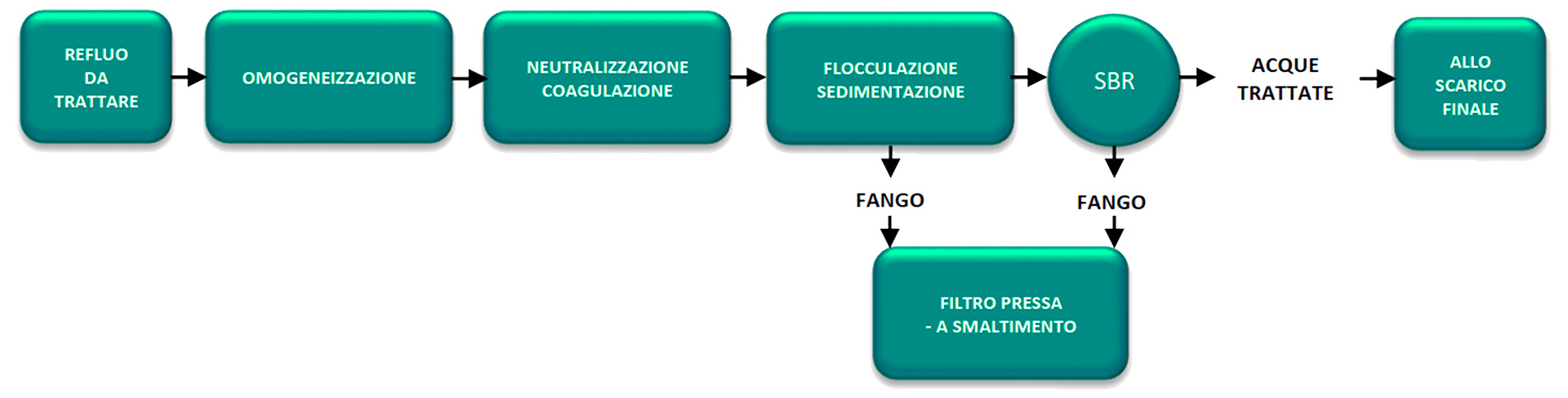
PHYSICAL CHEMICAL PRETREATMENT 30 m³/h
Homogenization: The effluent is sent to a storage and homogenization tank with a volume of about 3000 m³ in which floating agitators are installed for mixing.
Coagulation-neutralization: The effluent is sent to a first section of the plant where the coagulation and neutralization stages take place in succession.
Flocculation – lamellar decantation: in the flocculation section next decantation, separation of suspended solids from the clarified is achieved, which is then sent to the final biological treatment The sludge extracted from the bottom of the decanter is sent to the final filter press.
BIOLOGICAL 240 m³/g
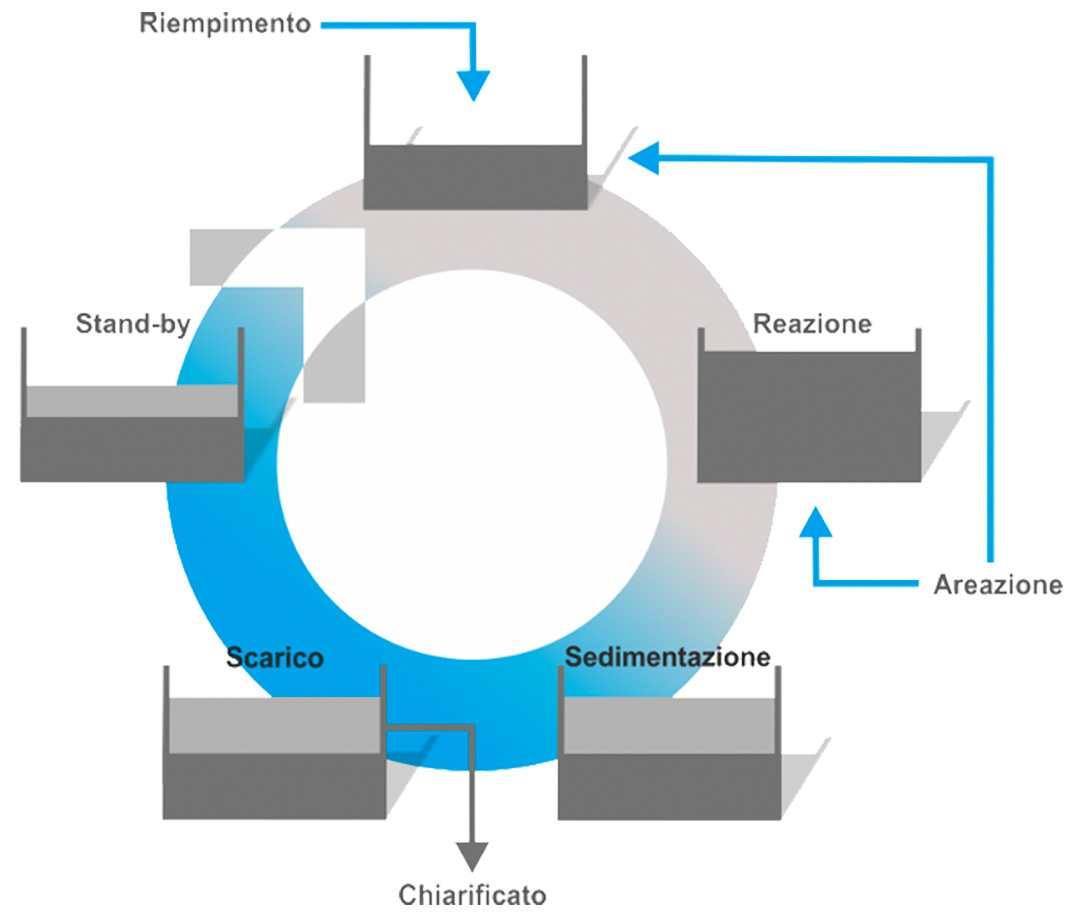
The biological section consists of an SBR reactor in which the different stages of treatment (homogenization, oxidation, denitrification, and sedimentation) occur in a temporal sequence and not spatially as in traditional biological plants (CAS, MBR, MBBR)
THE BENEFITS.
- High resistance to changes in organic input load;
- Absence of recirculation of both the activated sludge, as there is no settling tank, and the aerated mixture during the denitrification phase;
- High flexibility, as it is possible to change the duration of the different treatment stages, adapting them to the actual characteristics of the effluent to be treated;
- Smaller footprint than conventional biological plants;
- Quick installation of the biological reactor made of vitrified steel. It is only necessary to provide a concrete slab for the placement of the reactor;
- Ability to control and manage the plant remotely via PLC networking;
- Low consumption of chemical reagents and electricity.